A Power of Attorney for Health, also known as a healthcare proxy or healthcare power of attorney, is a legal document that allows an individual (the principal) to appoint someone they trust (the agent or attorney-in-fact) to make healthcare decisions on their behalf if they become unable to do so due to illness, injury, or incapacity. The purpose of this document is to ensure that the principal’s healthcare wishes are honored and that decisions about their medical treatment, end-of-life care, and other healthcare matters are made according to their preferences and values.
The importance of a Power of Attorney for Health cannot be overstated, especially in situations where the principal is unable to communicate their wishes regarding medical treatment. By appointing a trusted agent through this legal document, individuals can have peace of mind knowing that their healthcare decisions will be made by someone who understands their values, beliefs, and preferences. This document not only empowers the agent to act on behalf of the principal but also provides clarity and guidance to healthcare providers, ensuring that the principal’s wishes are followed even in challenging circumstances.
Furthermore, a Power of Attorney for Health allows individuals to plan for unforeseen medical emergencies or situations where they may lack the capacity to make informed decisions about their healthcare. It provides a structured framework for decision-making and helps avoid potential conflicts or disagreements among family members or healthcare providers regarding the appropriate course of action.
Table of Contents
TogglePower of Attorney For Health
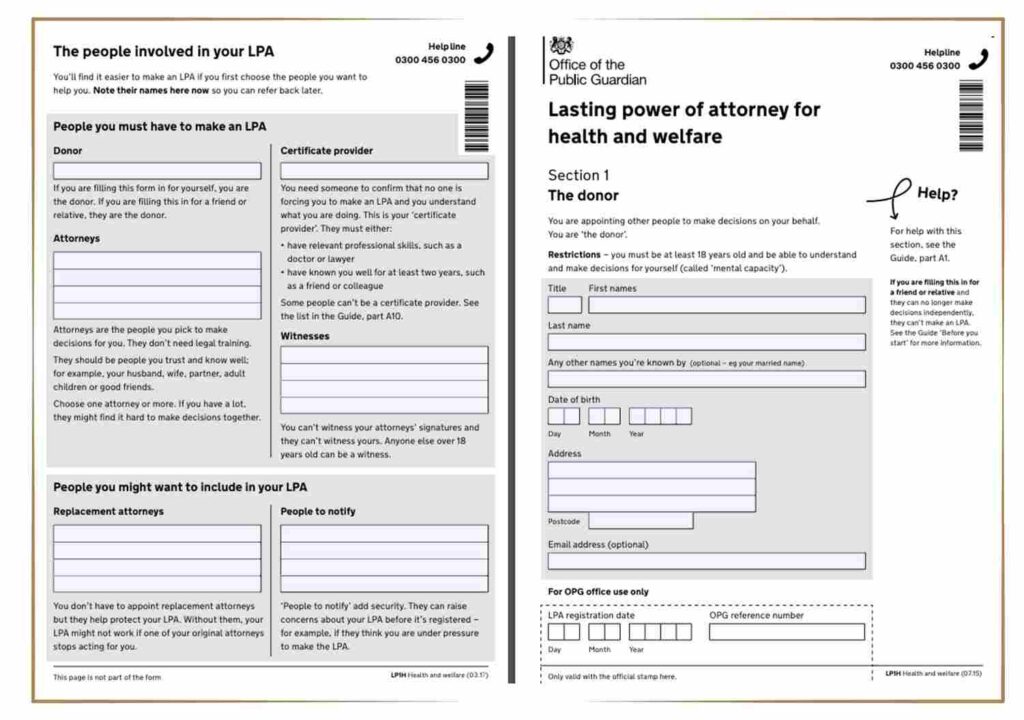
The concept you’re discussing closely resembles the Health and Welfare Lasting Power of Attorney (LPA) in England. Despite minor terminology differences (“Power of Attorney for Health” vs. “Health and Welfare LPA”), both serve the same primary purpose.
Here’s an outline detailing Health and Welfare LPAs in England:
- Function: A Health and Welfare LPA is a legal instrument enabling the donor to designate trusted individuals (attorneys) to make health and well-being decisions if the donor lacks mental capacity.
- Decisions Covered: Attorneys can decide on:
- Medical treatment (consent or refusal)
- Care home placement
- Daily care routines (e.g., meals, medication)
- Importance: A Health and Welfare LPA ensures your care preferences are honored if you can’t express them yourself.
- Key Differences from US Healthcare Power of Attorney:
- Terminology: The US uses “Power of Attorney” broadly, while England specifies “Lasting Power of Attorney” (LPA).
- Types of LPAs: England differentiates between property/financial affairs and health/welfare LPAs.
- Creating a Health and Welfare LPA in England:
- Download free LPA forms from GOV.UK (select “Health and Welfare”).
- Complete forms carefully per guidance.
- Select trustworthy attorneys understanding your wishes.
- Consider optional registration with the Office of the Public Guardian (OPG) for convenience.
- Additional Considerations:
- Legal consultation is advised for complexity or form completion doubts.
- Choose attorneys thoughtfully due to the LPA’s legal significance.
Understanding Health and Welfare LPAs ensures your health and care preferences are upheld effectively in the future.
How To Activate Power of Attorney For Health and Welfare?
In England, a Health and Welfare Lasting Power of Attorney (LPA) does not require a formal “activation” process. However, several important considerations enable your attorney(s) to use the LPA effectively:
Key Points for Utilizing a Health and Welfare LPA:
- Mental Capacity: The LPA becomes operational when you, as the donor, are no longer capable of making health and welfare decisions independently.
- Registration (Optional but Recommended): Although not obligatory, registering the LPA with the Office of the Public Guardian (OPG) is highly recommended. This registration creates a central record and facilitates your attorney(s) in demonstrating the LPA’s legitimacy to healthcare professionals. How Your Attorney Can Implement the LPA:
- Upon meeting the prerequisites mentioned above, your attorney(s) can present either the original LPA or a certified copy to healthcare providers involved in your treatment.
- The LPA delineates the specific powers granted to your attorney(s) concerning your health and well-being choices.
- Your attorney(s) are bound by a legal obligation to adhere to the LPA’s directives and act in your best interests, taking into account your expressed wishes and values in the document. Additional Information:
- Registration Process: If the LPA has not been registered yet, your attorney(s) can undertake the registration process with the reference number and activation key provided during the LPA’s creation (applicable to LPAs registered on or after July 17, 2020). Information regarding the registration process is available here: https://www.gov.uk/power-of-attorney/make-lasting-power
- Complex Situations: Disagreements regarding the LPA’s validity or your attorney’s decisions may necessitate involvement from the Court of Protection. Seeking advice from a solicitor can be beneficial in navigating such complexities. Here are some resources for further information:
- GOV.UK – Lasting Power of Attorney: https://www.gov.uk/power-of-attorney
- Office of the Public Guardian (OPG): https://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/office-of-the-public-guardian Understanding the operational aspects of Health and Welfare LPAs in England equips your attorney(s) with the necessary capabilities to make informed decisions concerning your care if you lose mental capacity.
Power of Attorney For Health And Welfare
A Health and Welfare Lasting Power of Attorney (LPA) in England aligns with the concept of a Health Care Power of Attorney in other jurisdictions. It enables individuals to appoint trusted representatives (attorneys) through a legal document, granting them authority over health and well-being decisions in case the donor loses mental capacity. Here’s an overview of Health and Welfare LPAs in England:
- Definition of Health and Welfare LPA:
- A Health and Welfare LPA allows the donor to appoint trusted attorneys to make decisions concerning their health and well-being if they become incapable due to mental incapacity.
- Decisions Covered by the LPA:
- Medical Treatment: Attorneys can consent to or refuse specific medical procedures, medications, or surgeries.
- Care Arrangements: They can determine your placement in care facilities based on your needs and preferences.
- Daily Care Routines: Attorneys can decide on your daily routine, including meals, medication administration, and personal hygiene.
- Importance of Health and Welfare LPAs:
- Ensures that your preferences regarding health and care are honored even when you can’t communicate them.
- Provides peace of mind for you and your loved ones regarding your well-being.
- Creating a Health and Welfare LPA:
- Choose Trustworthy Attorneys: Select individuals who understand your wishes and are comfortable making healthcare decisions on your behalf.
- Obtain and Complete Forms: Download and fill out the free LPA forms carefully, including witness signatures as required.
- Decide on Activation: Indicate when the LPA should be effective, immediately or upon loss of mental capacity.
- Optional Registration: While not mandatory, registering the LPA with the Office of the Public Guardian (OPG) is advisable for ease of use.
- Using the Health and Welfare LPA:
- Mental Capacity: The LPA becomes operational when you lose the ability to make health decisions.
- Registration Benefits: Although optional, registration simplifies validation for healthcare professionals.
- Attorney’s Role: Attorneys must follow LPA instructions and act in your best interests, considering your expressed wishes.
Understanding Health and Welfare LPAs ensures that your health preferences are upheld during times of incapacity, emphasizing the importance of careful planning and selecting reliable attorneys.
Power of Attorney For Health Care
The concept of a “Power of Attorney for Health Care” (also known as Healthcare Power of Attorney or Medical Power of Attorney) is widely recognized globally, although the specific legal mechanisms and procedures for appointing someone to make healthcare decisions can vary depending on the jurisdiction.
Here’s an overview of this concept and some essential points to consider:
- Core Function:
- A Power of Attorney for Health Care enables the principal (you) to designate a trusted individual (attorney-in-fact or healthcare agent) to make medical decisions if you’re unable to do so due to illness, injury, or incapacity.
- Decisions Covered:
- The decisions your attorney-in-fact can make will be outlined in the document and governed by local laws. These decisions may include:
- Consenting to or refusing medical treatments such as surgery or medication.
- Selecting the level of care, such as comfort care or aggressive treatment.
- Choosing a care facility like a nursing home.
- The decisions your attorney-in-fact can make will be outlined in the document and governed by local laws. These decisions may include:
- Benefits:
- Ensures that your healthcare preferences are honored even when you can’t express them.
- Provides reassurance for you and your loved ones.
- Empowers your attorney-in-fact to make informed decisions aligned with your values and wishes.
- Creating a Power of Attorney for Health Care:
- Select Your Attorney-in-Fact: Choose someone trustworthy who understands your values and is willing to act on your behalf. Discuss your preferences with them beforehand.
- Obtain and Complete the Forms: These forms may be available from healthcare providers or legal professionals. Follow the instructions carefully, including any requirements for witness signatures.
- Legal Validity: Ensure the document complies with your jurisdiction’s legal requirements. Consulting a lawyer familiar with local laws is advisable.
- Additional Considerations:
- Living Will: Consider whether you also need a living will, which expresses your specific medical treatment preferences.
- State-Specific Laws: Laws governing Powers of Attorney for Health Care can vary by state or country. Seek legal advice to ensure your document is legally binding.
Researching and understanding the requirements and procedures for a Power of Attorney for Health Care in your jurisdiction is essential. Consulting with legal professionals or healthcare providers can provide further guidance and ensure your document is valid and effective.
FAQ
What is a Power of Attorney for Health and Welfare (Healthcare Power of Attorney)?
A Power of Attorney for Health and Welfare (also known as a Healthcare Power of Attorney or Medical Power of Attorney) is a legal document that allows you (the principal) to appoint a trusted person (the attorney-in-fact or healthcare agent) to make decisions about your health and well-being if you become unable to do so yourself due to illness, injury, or mental incapacity.
Here’s a closer look at how it works:
What Decisions Can Your Attorney Make?
The decisions your attorney-in-fact can make will depend on the specific document and local laws, but generally include:
- Medical Treatment: Consenting to or refusing specific medical procedures, medications, or surgeries.
- Care Arrangements: Choosing your placement in a care home, assisted living facility, or other care setting.
- Daily Care Routines: Making decisions about your daily routine, such as meals, medication administration, and personal hygiene care.
Benefits of Having a Power of Attorney for Health and Welfare:
- Ensures your wishes are respected: Even if you can’t communicate your preferences, your attorney can make decisions aligned with your values.
- Provides peace of mind: Knowing your well-being is looked after in case of incapacity offers peace of mind for you and your loved ones.
- Empowers your attorney: It allows your chosen representative to make informed decisions based on your best interests.
Creating a Power of Attorney for Health and Welfare:
The process for creating this document can vary depending on your location. Here’s a general outline:
- Choose Your Attorney-in-Fact: Select a trustworthy individual who understands your values and is comfortable making healthcare decisions on your behalf. Discuss your wishes with them beforehand.
- Obtain and Complete the Forms: These may be available from your doctor’s office, hospital, or legal professional. Follow the instructions carefully.
- Witness Signatures: Some jurisdictions require witness signatures from qualified individuals.
- Validity: Check with a lawyer to ensure the document meets your local legal requirements.
Additional Considerations:
- Living Will: While a Power of Attorney for Health and Welfare focuses on broad decision-making, a living will is a separate document that expresses your wishes regarding specific medical treatments (e.g., life support). Some jurisdictions may combine these into a single document.
- Local Laws: Laws governing Powers of Attorney for Health and Welfare differ by country and state. Always consult with a lawyer familiar with your local laws to ensure your document is valid and enforceable.
In Conclusion:
A Power of Attorney for Health and Welfare is a crucial tool for ensuring your well-being is protected if you lose the ability to make decisions for yourself. By understanding how it works, you can take control of your future healthcare and provide peace of mind for yourself and your loved ones. Remember, research the specific requirements and procedures in your area to create a valid and enforceable document.
What decisions can my attorney-in-fact make with a Health and Welfare Power of Attorney?
Having a Health and Welfare Power of Attorney (HWPA) enables your attorney-in-fact to make crucial decisions about your health and well-being if you’re unable to do so. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the key areas where your attorney can act on your behalf:
- Medical Treatment Decisions:
- Consenting or Refusing Procedures: Your attorney can approve or decline medical treatments, including surgeries, medications, and other procedures, based on your expressed wishes or discussions.
- Choosing Care Levels: They can decide on the level of care you receive, balancing factors like potential benefits, risks, and your overall comfort. For instance, they may opt for comfort-focused care rather than aggressive treatments if that aligns with your preferences.
- Pain Management: Your attorney can manage decisions related to pain relief measures and other strategies to enhance your comfort.
- Care Arrangements:
- Facility Placement: If necessary, your attorney can select an appropriate care facility like a nursing home or assisted living facility, taking into account your preferences and needs.
- Daily Care Routines: They can oversee your day-to-day care activities such as meals, medication schedules, personal hygiene, and other aspects impacting your well-being.
- Additional Considerations:
- Specific Powers Granted: The extent of your attorney’s authority is defined in the HWPA document. You can specify the types of decisions they can make or provide broader decision-making power within the health and welfare framework.
- Following Your Wishes: It’s crucial for your attorney to act in your best interests and honor your expressed wishes or previous discussions outlined in the HWPA document. Effective communication beforehand is essential.
Limitations to Note:
- Financial Decisions: HWPA typically doesn’t cover financial matters. A separate Power of Attorney for Property and Financial Affairs may be required for managing finances.
- Personal Decisions Beyond Healthcare: Decisions like marriage or residential choices are generally not within the scope of a Health and Welfare Power of Attorney.
In essence, a Health and Welfare Power of Attorney empowers your chosen representative to make informed decisions about your health and well-being according to your preferences and best interests when you’re unable to do so. It offers peace of mind for you and your loved ones, ensuring your well-being is managed as per your wishes.
Do I need a lawyer to create a Power of Attorney for Health and Welfare?
In most instances, you may not require legal assistance to create a basic Health and Welfare Power of Attorney (HWPA). Here’s a breakdown of the factors to consider:
- When a Lawyer May Not Be Necessary:
- Straightforward Circumstances: If your situation is uncomplicated and you seek a standard HWPA without intricacies, you can potentially create it independently. Many areas provide free downloadable forms on government or healthcare institution websites.
- Clear Instructions: If the forms are straightforward and you can clearly articulate your wishes, crafting a basic HWPA might be feasible without legal counsel.
- Benefits of Legal Consultation:
- Legal Expertise: A lawyer specializing in estate planning and Powers of Attorney ensures your HWPA complies with legal standards and is enforceable in your jurisdiction. This is crucial for complex situations or if you have uncertainties about legal aspects.
- Guidance and Customization: Legal professionals offer guidance, explain options, and assist in tailoring the HWPA to suit your specific requirements.
- Understanding Local Laws: Laws regarding Powers of Attorney vary by region. Lawyers ensure your HWPA adheres to local legal criteria.
- Peace of Mind: Having a lawyer draft your HWPA provides assurance that it accurately reflects your wishes and complies with legal norms.
- Situations Requiring Legal Consultation:
- Complexities: Legal expertise is vital for situations involving existing medical conditions, potential family conflicts, or other complexities.
- Specific Limitations: If you wish to impose precise restrictions on your attorney’s authority, a lawyer can draft the document clearly to prevent misunderstandings.
- Large Estates: Considering a lawyer for your HWPA is advisable when managing substantial estates as part of comprehensive estate planning.
Ultimately, the decision to engage a lawyer depends on your comfort level with legal matters, the complexity of your situation, and your desire for a robust HWPA that accurately reflects your wishes.
Is registration of a Health and Welfare Power of Attorney mandatory?
No, registering a Health and Welfare Power of Attorney (HWPA) is not obligatory in England. However, opting to register your HWPA with the Office of the Public Guardian (OPG) is strongly advised for several reasons:
Advantages of Registering a Health and Welfare LPA:
- Enhanced Accessibility for Your Attorney: A registered HWPA (also referred to as a Health and Welfare Lasting Power of Attorney – LPA) simplifies usage for your attorney(s). Healthcare professionals can swiftly authenticate it through the OPG online register, streamlining the process and preventing potential delays in crucial healthcare decisions.
- Reduced Dispute Risk: A registered HWPA establishes a clear record of your intentions, minimizing the likelihood of conflicts or challenges from family members or healthcare professionals concerning your attorney’s authorization.
- Peace of Mind: Registration of your HWPA assures both you and your loved ones of a smoother pathway for your attorney to act on your behalf in healthcare matters, providing reassurance if such actions become necessary. Registration Process Overview:
- The donor or their appointed attorney(s) can initiate registration with the OPG following the completion and signing of the HWPA by all relevant parties.
- There is a current registration fee of £82 (as of April 2, 2024) for each LPA.
- The OPG will assess the document and proceed with registration if all requirements are met, issuing a unique reference number for future reference. Although registration is not compulsory, its associated benefits render it a highly advisable step.
For additional information on registering a Health and Welfare LPA in England, consult the following resources:
- GOV.UK – Power of Attorney: https://www.gov.uk/power-of-attorney
- Office of the Public Guardian (OPG): https://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/office-of-the-public-guardian

Hello, I’m Inna Evdokimova, an IP Lawyer and Patent Attorney based in the United Kingdom. With a passion for intellectual property law, I specialize in providing expert guidance and legal representation to clients navigating the complexities of patent law in the UK.
With years of experience in the field, I’ve cultivated a deep understanding of the intricacies of intellectual property rights, empowering individuals and businesses alike to protect their innovations and creations effectively.
Through my website, powerofattorneyuk.uk, I aim to serve as a valuable resource for those seeking clarity and assistance in matters of patent law and intellectual property rights. Whether you’re looking to secure a patent for your invention or require guidance on IP-related legal issues, my mission is to provide you with personalized, reliable solutions tailored to your unique needs.
I’m dedicated to helping my clients safeguard their intellectual property assets and navigate the legal landscape with confidence. With a commitment to excellence and client satisfaction, I strive to deliver results-driven strategies and advocacy that exceed expectations.
I look forward to the opportunity to assist you on your intellectual property journey and help you unlock the full potential of your innovations.